Since our last update, there have been significant international and domestic events which have impacted shipping. China’s energy rationing has reduced the demand for outbound freight while, domestically, the Industrial action between Patrick’s and the Maritime Union of Australia has increased delays at Australian wharves.
Over the last month, 20 of China’s 31 Provinces have implemented strict power restrictions, which will result in a reduction in manufacturing and exports. The Shanghai containerised Freight Index reflects this, having, in essence, remained steady for all of October, fluctuating between 4614 at the start of October to 4583 now (see fig. 1.0).
Unfortunately, this paints a better picture than what can be predicted. Any disruptions or significant change to the supply chain will likely increase bottlenecks, change schedules, and finally, increase delays to supply and raised costs. Maersk, the worlds largest Container Line, stated, “This may harm supply chains”.
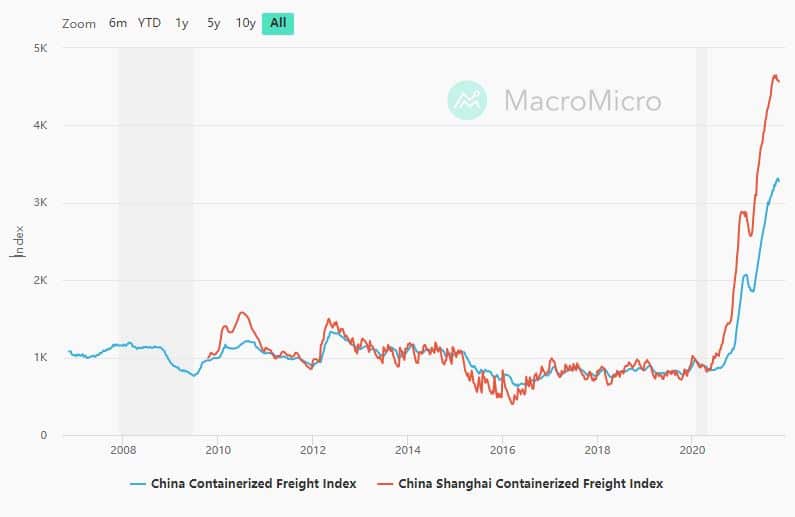
Fig.1.0 CCFI is based on the freight rate and volume of 12 routes around the world, reflecting changes in freight rate. Departing ports include ports of Dalian, Tianjin, Qingdao, Shanghai, Nanjing, Ningbo, Xiamen, Fuzhou, Shenzhen and Guangzhou.
Locally, the ongoing industrial action between Patricks Terminals and the Maritime Union of Australia (MUA) has further escalated with Patrick’s attempting to have the Enterprise Agreement terminated. MUA have retaliated with further industrial action, adding to the over 220 Industrial activities undertaken since negotiations.
These developments will further increase delays to vessel schedules, which have already had ships in Sydney wait up to eighteen days to berth, nine days in Melbourne, eight in Brisbane and three in Fremantle —in turn, reducing the total amount of shipping containers able to reach the Australian market.

Aerial view of the Port Botany in Sydney, one of the affected ports facing increase delays to vessel schedules.
As a direct example, the MUA has refused to unmoor a vessel for 48 hours. The ship does a specific rotation between Singapore and Fremantle that 48 hours waiting if happened consistently would reduce capacity on this lane by 15%.
While industrial action continues at Australian ports, further delays and vessels being forced to skip planned ports will, unfortunately, continue.
Overall, Redox predicts ongoing changes to the supply chain over the coming 12 months. While there is ever instability and disruption, prices will not reduce, and reliability will not improve.
Please continue to stay in close contact with your Redox Representative to discuss a range of strategies to reduce risk to your supply chain and to further understand how pricing and reliability will affect your business during the coming 18 months.