Flotation reagents are a crucial processing technology that has remained relatively unchanged since its introduction, though It has seen numerous advancements in both use, technology, and reagents over the years.
Then and now
Initially employed in the mining and mineral processing sectors, it was one of the most significant 20th century enabling technologies. The ancient Greek, Persian, and Egyptian writings are among the earliest indications of this technology’s antiquity.
However, contemporary flotation methods are more a testament to significant technological advancements in flotation chemistry and chemicals than hardware and manual labour.
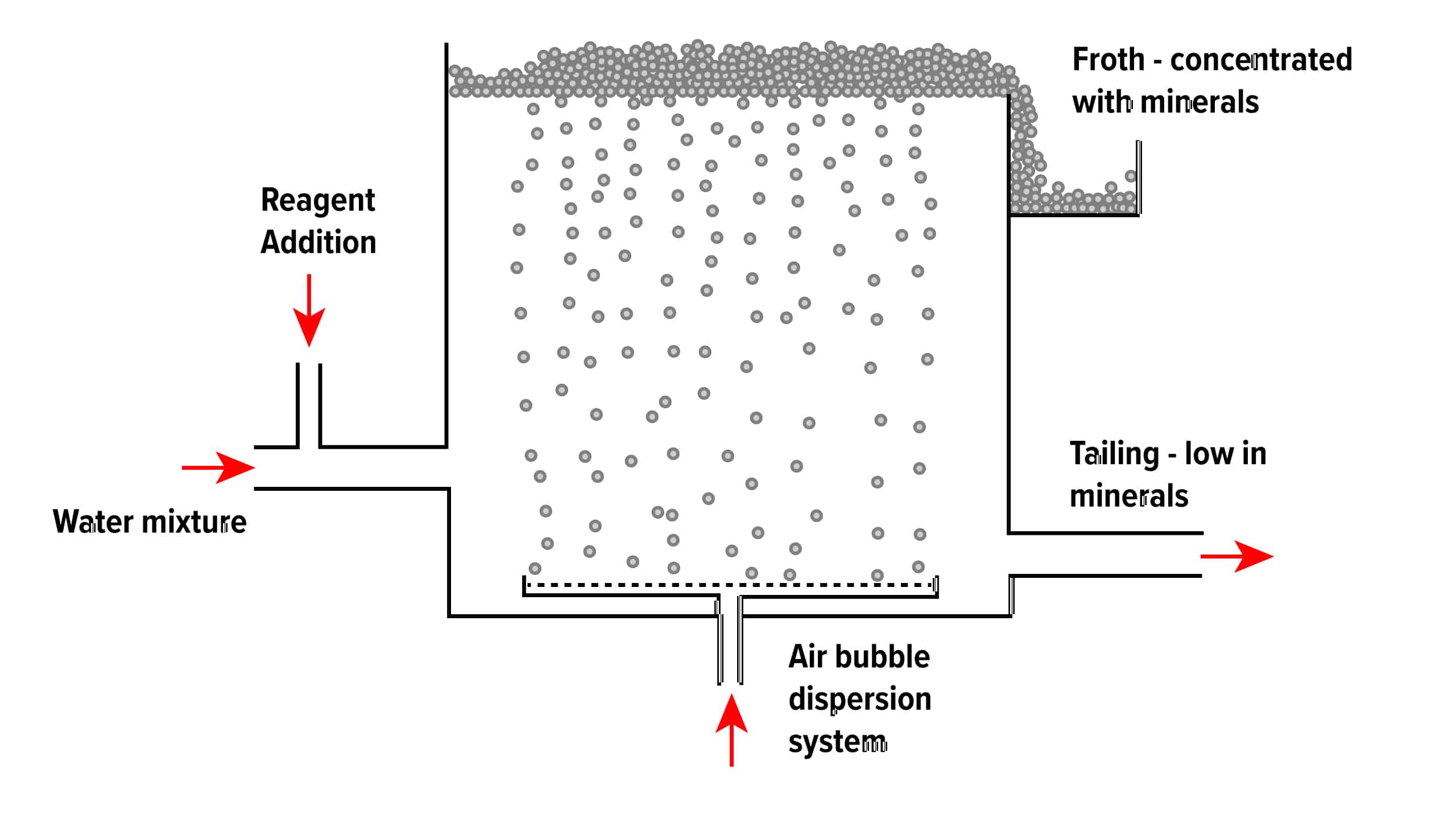
The froth flotation process is about taking advantage of the natural hydrophobicity of liberated (well ground) minerals/metals and making/playing on making them hydrophobic (water-repel) individually to carefully separate them from one another and the slurry they are in.
Mineral Processing
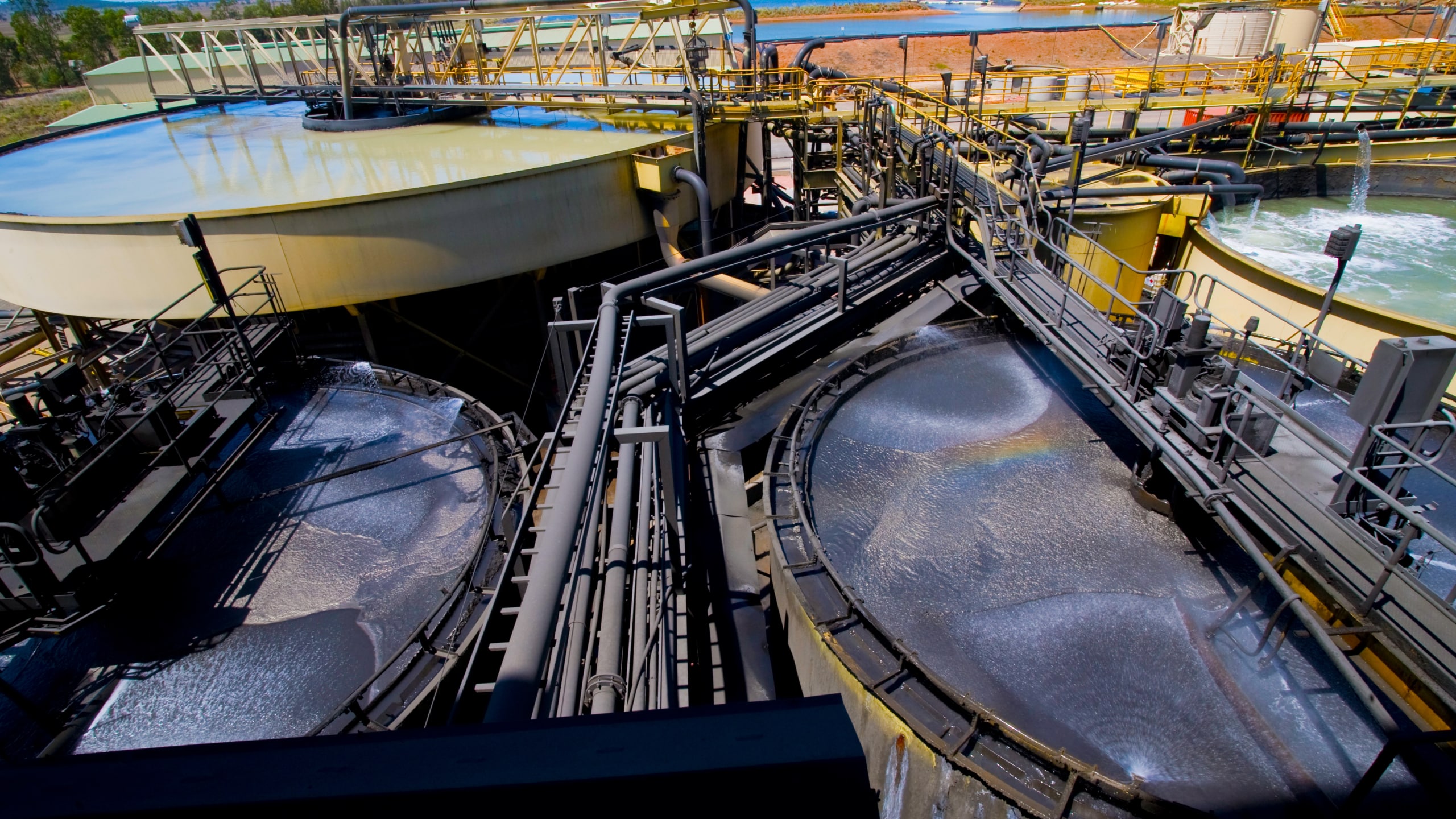
Froth flotation is a method of separating minerals from gangue by exploiting differences in hydrophobicity. Wetting agents and surfactants are used to make the hydrophobic distinctions between valuable material and waste gangue possible.
The selective separation of the minerals makes processing mixed ores a more economically feasible task. It is particularly effective in treating fine minerals and solves the complex recovery process of valuable components in many fine mineral particles. The flotation process separates an extensive range of sulphides, carbonates and oxides before further refinement.
Flotation has advanced considerably in the last decade, introducing froth flotation equipment, froth flotation reagents, and froth flotation technology. These advances have contributed to more than 60% – 70% of the ore in the world being separated by the froth flotation method.
The development of froth flotation has improved the recovery of valuable minerals, such as copper- and lead-bearing minerals. Along with mechanized mining, it has allowed the economic recovery of valuable metals from much lower grade ore than previously possible.
Some of the advantages of the froth flotation method include:
- It’s one of the most popular methods, which enjoys a near-monopoly in several mineral processing technologies.
- It can be used to process a variety of nonferrous metals, rare metals, and non-metallic minerals.
- High separation efficiency, especially suitable for low grade, fine grain size minerals.
Different Classifications
Flotation reagents are classified according to the role they play in flotation. Collectors, frothers, regulators, and depressants are used as classifications for such reagents.
- The collector’s function is to take from a hydrophobic layer on a mineral surface in the flotation pulp and create conditions for the attachment of the hydrophobic particles to air bubbles and recovery of particles in the froth product.
- Surface-active frothers are heteropolar surface-active chemicals that decrease the surface tension of water and have the ability to adsorb on the air bubble–water interface. Their presence in solution increases the film strength of air bubbles, allowing for better hydrophobic particle attachment.
- Activators, depressants, and pH regulators are often referred to as modifiers or regulators of the flotation process. The main purpose of these reagents is to modify the action of the collector on mineral surfaces and therefore govern the selectivity of the flotation process. In the presence of regulators, the collector only adsorbs on particles that are targeted for recovery.
How can we help?
It’s essential to work with a supplier that can guarantee consistent quality; Redox can supply within Australia, New Zealand, and the United States and is in a great position to meet and exceed your expectations; contact one of our industry specialists today.
