Gut health is important for weaning piglets, in particular when the high dosage of ZnO and antibiotics are removed from piglets feeds..
Apart from the dietary nutrients’ digestion and absorption, the gut is the largest immune organ in pigs and can be divided into four protection layers (Figure 1, Gao et al, 2020).
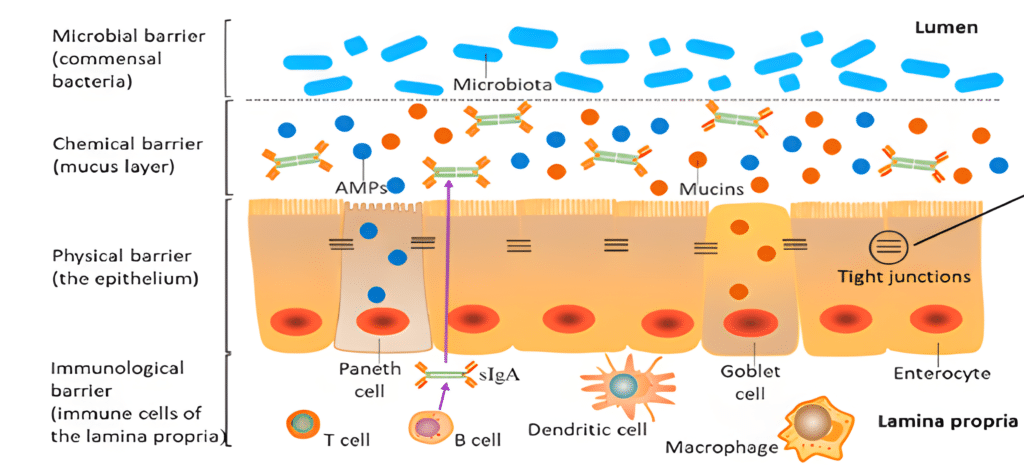
Figure 1. The different protective layers of the intestinal barrier
The commensal bacterial barrier is a complex environment playing a key role in maintaining the gut health; the chemical barrier consists of the mucus layer secreting mucins and antimicrobial peptides; the physical barrier is composed of epithelial cells and the immunological barrier harbouring the immune cells that secreted immune mediators such as cytokines and antibodies.
Traditionally bile acids are bio-surfactants, assisting intestinal digestion and absorption of lipids and fatty soluble vitamins such as Vitamin A, D, E and K, and thereby improving nutrient utilization. Recently, in the gut epithelial cell, bile acids are identified as signalling molecules to activate a couple of nuclear receptors, namely farnesoid X receptor (FXR), pregnane X receptor (PXR), Vitamin D receptor (VDR) and G-Protein coupled receptor (TGR5). Therefore, bile acids play an important role in regulating epithelial barrier functions.
In 2018, Ipharraguerre et al indicated that currently all alternatives including probiotics, prebiotics, organic acids, essential oils, antimicrobial and plants extracts to antibiotics or high dosage of ZnO underlined their growth promotion action. They demonstrated that either antibiotics or the high dosage of ZnO could activate bile acids receptors and consequently spare nutrients for growth and improve the metabolic efficiency of antibiotics or the high dosage of ZnO treated animals. Therefore, it is necessary for adding the exogenous bile acids to antibiotics free or the high dosage ZnO free diets in weaning piglets.
Based on experimental data in China, Belgium, adding 350 grams per MT feed commercially available exogenous bile acids could improve daily weight gain by 9% and FCR by 7 points.
Report by Redox Animal Nutritionists