Taurine is a β-amino acid containing a sulfonate instead of a carboxylic group in α-amino acids. It is vital for organ development and aging but not for protein synthesis. Taurine is needed for membrane stabilization, has cytoprotective and cell volume regulation effects, and maintains calcium homeostasis and signalling.
Aquatic feeds for farmed fish and shrimp are mainly made from protein rich ingredients such as fish meal, poultry by-product meal, soybean meal concentrate, yeast protein, pea protein concentrate, corn gluten meal and wheat gluten meal.
Historically fish meal has been the protein source of choice and currently there is no alternative to replace fish meal completely. It is probably since most alternative ingredients are deficient in one or more of the ten essential amino acids: lysine, methionine, threonine, valine, isoleucine, leucine, tryptophan, histidine, arginine, and phenylalanine. However, due to the high price and tight supply of fish meal, a steady decline of fish meal inclusion levels in aquacultural feeds has pushed higher inclusion levels of alternative protein rich ingredients supplemented crystalline essential amino acids.
Histidine is an integral component of a broad set of tissues including skin, bone, ligaments, and muscle. It also stimulates the digestive secretion of gastrin, a hormone that is essential for digestion of dietary protein. Histidine deficiency could induce a decrease in amino acids oxidation and a decrease protein turnover. For Atlantic salmon, it is reported that a minimum dietary histidine concentration of 1.4% is needed for the prevention of cataracts. Compared with fish meal, usually animal protein alternatives contain less histidine (Table 1). In Table 1, it is also clearly shown that using wheat gluten meal to replace soy protein concentrate might obtain similar histidine concentration but lower arginine concentration to that in fish meal.
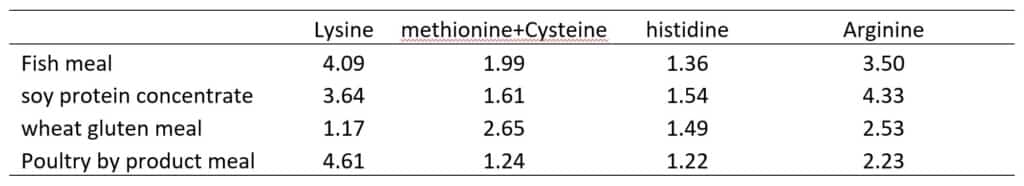
Table 1 some essential amino acids in protein rich ingredients (%)
Histidine is an amino acid that has the most powerful impact on fish palatability and providing adequate levels of histidine is critically important for fish or shrimp growth. For shrimps, the dietary requirement of histidine is about 0.8%, corresponding to 2.2% dietary crude protein level. For Rainbow trout, the dietary requirement of histidine is about 0.6%, corresponding to 1.2% crude protein level. For Nile tilapia, the dietary requirement of histidine is about 1%, corresponding to 1.7% protein level. To prevent leaching of crystalline histidine, fish or shrimp diets can be bound with carboymethylcellulose, corn starch and K-carrageenan.