One of the most powerful solutions to ensure a safe mine environment is fire retardant anti-static (FRAS) materials, which protects against all kinds of hazardous situations like fuel fires or explosions caused by heat build-up, static sparks, and other combustible substances that could seriously compromise your mine’s safety.
Materials such as rubber, polyurethane, PVC, polyethylene, polypropylene and polyester are often used to make base materials that are then manufactured into products for underground coal mining. Fibre-reinforced resin materials such as fibreglass and carbon fibre composite are also used.
The products manufactured include ventilation sheeting (brattice) and ventilation stoppings, ventilation ducting (rigid and flexible), dust curtains, venturi blowers, air fans, pipes, conveyor belting and conveyor accessories.
Recommendations on FRAS materials
Mine operators of underground coal mines must ensure that control measures are implemented for products subject to the accumulation of static charge. The control measures should include the following:
- Procedures to verify the products are installed per the manufacturer’s directions for static discharge.
- Appropriate measures are implemented to ensure that the properties of FRAS materials are maintained over time.
Manufacturers of FRAS-rated materials must ensure that testing is undertaken in accordance with the relevant requirements of MDG 3608 by an independent testing facility for:
- All FRAS material intended for use in an underground coal mine
- Any change of material composition or manufacturing technique for a FRAS-rated material, including changes of colour, to verify the suitability of the material.
Manufacturers and suppliers of products incorporating FRAS materials as components must ensure that:
- The product’s design incorporates suitable controls to prevent the accumulation of a static charge on the FRAS components.
- Instructions for the safe use of the product include mounting or suspension requirements to prevent the accumulation of a static charge on the FRAS components.
- Any change of material composition or change to the product design, including changes of colour, size or placement of eyelets, rivets or mountings, are tested in accordance with the relevant requirements of MDG 3608
- The product is suitably marked to indicate compliance with MDG 3608.
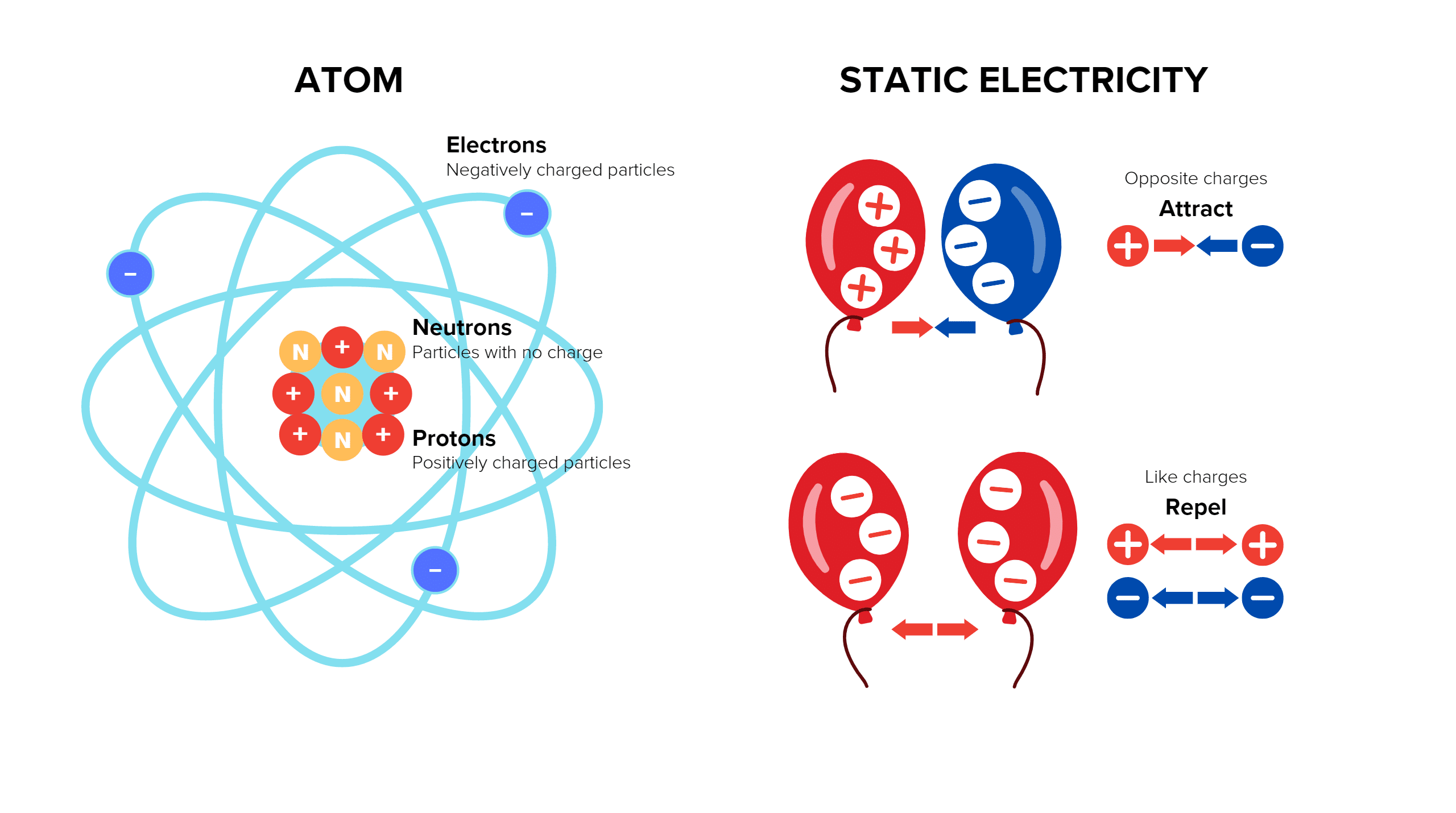
Every object is made of atoms that are typically electrically neutral. They contain an equal number of protons (positive charge) within their nucleus and electrons (negative charge) surrounding the nucleus. Static electricity occurs when there is a separation of positive and negative charges within or on the surface of a material or between materials. Electrons may move from one object to another, leaving one object with a negative charge and the other with a positive. When the objects are separated they retain the charge imbalance.
How can we help?
To minimise risks, improve occupational health and safety hazards, and, importantly, minimise underground ignitions, fire retardant anti-static (FRAS) materials are now required in all NSW underground mines, monitored by the NSW resources regulator.
Redox offers many polymer/composite options for differing FRAS application solutions.
Contact our Plastics division today if you would like to learn more about material solutions supported by our many international principal partners.